Understanding Carbide Insert Grades and Their Uses
Learn about carbide insert grades, ISO codes, coatings, and their applications in turning, milling, and CNC cutting tools. Discover how to select the right insert for your machining needs.
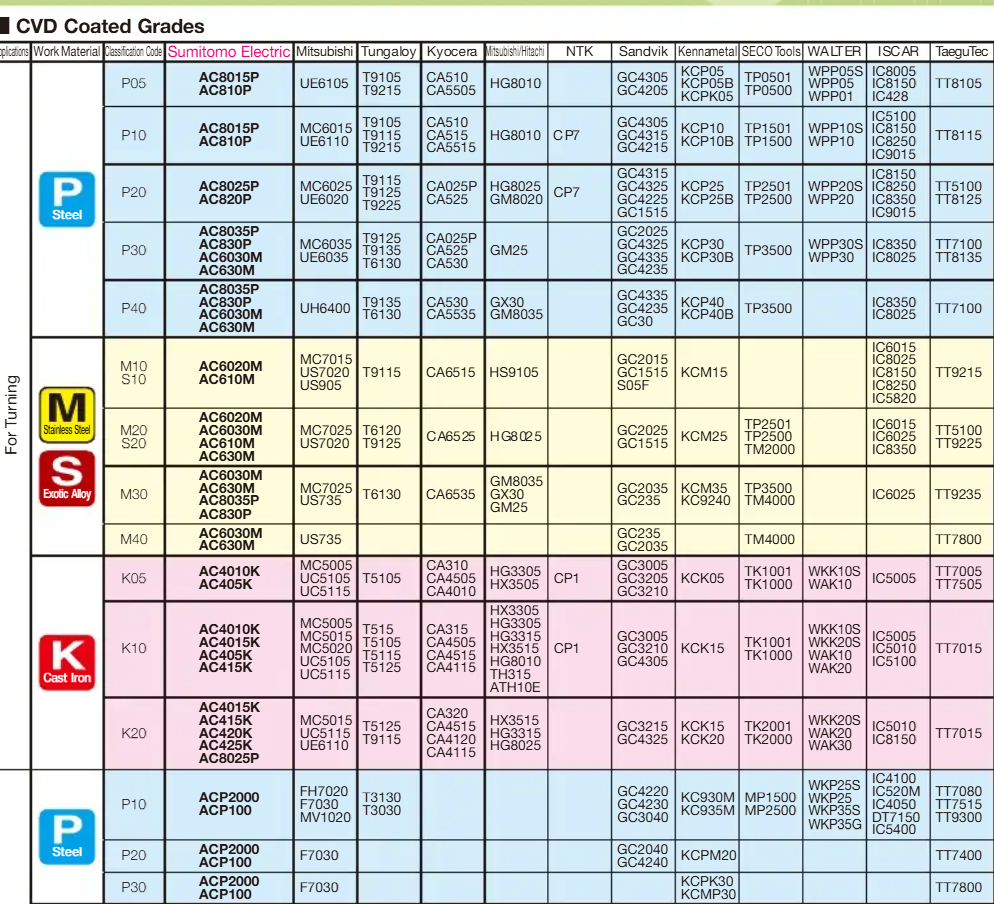
In the fast-paced world of CNC machining and metalworking, selecting the right carbide insert can make the difference between precision and costly errors. Carbide inserts are at the heart of modern machining, enabling high-speed cutting, longer tool life, and consistent quality across industries like automotive, aerospace, die & mold, and general manufacturing.
Understanding carbide insert grades, coatings, and ISO codes is crucial for machinists, engineers, and procurement specialists alike. This guide will help you navigate the technical landscape of turning and milling inserts, making your selection process easier and more accurate.
What Are Carbide Insert Grades?
Carbide insert grades define the composition, hardness, toughness, and wear resistance of an insert. Each grade is engineered for specific applications, workpiece materials, and cutting conditions.
- Hard grades: High hardness for cutting hardened steels and alloys.
- Tough grades: High impact resistance, ideal for interrupted cuts and roughing operations.
- General-purpose grades: Balanced hardness and toughness for versatile applications.
Example: Sandvik Coromant’s GC series offers a variety of grades:
- GC1015: General-purpose for steel.
- GC1025: Tough grade for interrupted cutting.
ISO Carbide Insert Nomenclature
ISO 1832 provides a standardized code to describe every aspect of a carbide insert. Reading these codes is essential to match the insert to your machining needs.
Example ISO Code: CNMG 120408
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| C | Insert shape: 80° diamond |
| N | Clearance angle: 0° (neutral) |
| M | Tolerance: medium |
| G | Manufacturing: ground insert |
| 12 | Insert size (inscribed circle in mm) |
| 04 | Thickness in mm |
| 08 | Nose radius in mm |
Key Takeaways
- Shape affects cutting forces and access to corners.
- Clearance angle determines how the insert contacts the workpiece.
- Tolerance ensures precision in finished parts.
- Chip breaker design improves chip evacuation and surface finish.
- Coating enhances wear resistance, heat resistance, and lubricity.
Types of Carbide Inserts by Application
Turning Inserts
- Use: External and internal turning on lathes or CNC turning centers.
- Materials: Steel, stainless steel, cast iron, non-ferrous metals.
- Example: CNMG or TNMG inserts with PVD or CVD coatings.
- Benefits: High precision, long tool life, consistent surface finish.
Milling Inserts
- Use: Face milling, shoulder milling, slotting on CNC milling machines.
- Materials: Aluminum, steel, titanium alloys.
- Example: Positive rake inserts like XOMX or OXMX series.
- Benefits: Efficient material removal, reduced vibration, improved chip evacuation.
Drilling & Special Inserts
- Use: Threading, grooving, parting, and specialty applications.
- Example: Kennametal or Taegutec threading inserts.
- Benefits: Precision for complex geometries, reduced tool changes.
Coating and Chip Breaker Considerations
Coatings:
- PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition): Thin, hard coating ideal for high-speed steel and stainless steel.
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Thicker coating, excellent for abrasive materials like cast iron.
Chip Breakers:
- Designed to control chip formation and prevent workpiece damage.
- Example: Sandvik’s “M-class” chip breaker ensures smooth machining of medium steel.
Analogy: Think of chip breakers as “road signs” guiding metal chips safely away from the cutting zone.
Brand Comparison (Neutral)
| Brand | Strengths | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik | Wide range, innovative coatings | Aerospace, automotive |
| Iscar | Precision inserts, unique geometries | Die & mold, high-speed machining |
| Kennametal | Robust grades, tough inserts | General machining, roughing |
All these brands follow ISO 1832, ensuring consistency in selection.
Practical Applications Across Industries
- Automotive: Engine blocks, shafts, and gear components using tough turning inserts.
- Aerospace: High-precision titanium and aluminum parts with coated milling inserts.
- Die & Mold: Complex cavity machining using ground inserts for fine tolerance.
- General Machining: Versatile grades for steel, stainless steel, and aluminum parts.
Conclusion
Selecting the right carbide insert grade is critical for productivity, cost efficiency, and quality. By understanding ISO insert nomenclature, coatings, chip breakers, and brand-specific features, you can make informed choices for turning, milling, and specialty applications.
Explore CNC Tools Depot’s extensive marketplace to find the perfect carbide inserts for your machining needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
CNMG indicates an 80° diamond-shaped insert with 0° clearance, medium tolerance, and a ground finish.
PVD-coated, tough grades like Sandvik GC4225 or Kennametal KCU series work best.
ISO codes (like CNMG 120408) detail shape, clearance, tolerance, chip breaker, size, thickness, and nose radius.
CVD coatings are thicker, ideal for abrasive materials, while PVD coatings are thinner, harder, and better for stainless steel and high-speed machining.
We stock top brands, offer verified technical data, and provide expert guidance for selecting the right insert every time.



